Credit Loan Default Prediction
Data Set Source
In 2018, the machine learning website Kaggle held a competition for ‘Kagglers’ to build a model that could predict if an individual would default on a loan within some timeframe – Home Credit Default Risk.
Towards the end of 2018 AIBMod was looking for a credit loan dataset with a large number of rows and features, but also with an unstructured data arrangement to reflect real life.
The input consisted of multiple files with many to one and none to one mappings between them.
These files are discussed more below the results.
The team that won the competition used an ensemble approach (common in machine learning competitions) consisting of various boosted trees and neural network models and a large amount of feature engineering to both create new features from the existing features and to transform the unstructured data into an input format which could be passed to such models.
A member of the winning team published code of a boosted tree model and how the model was trained on the data.
From AIBMod’s perspective, this was an ideal opportunity to highlight any deficiencies in the neural transformer model as set out in the original paper and then develop with the target of beating the performance of the LightGBM model – a boosted tree model.
The results comparison can be found below.
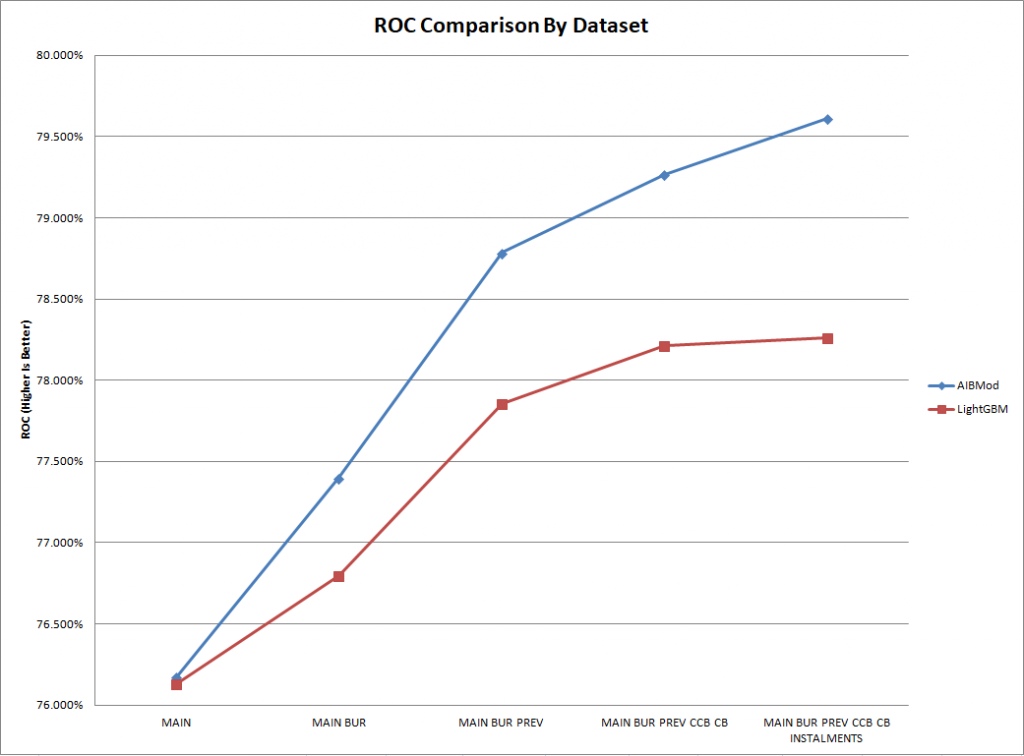
AIBMod vs Boosted Tree Results (ROC1)
AIBMod vs Boosted Tree Results (Logloss)
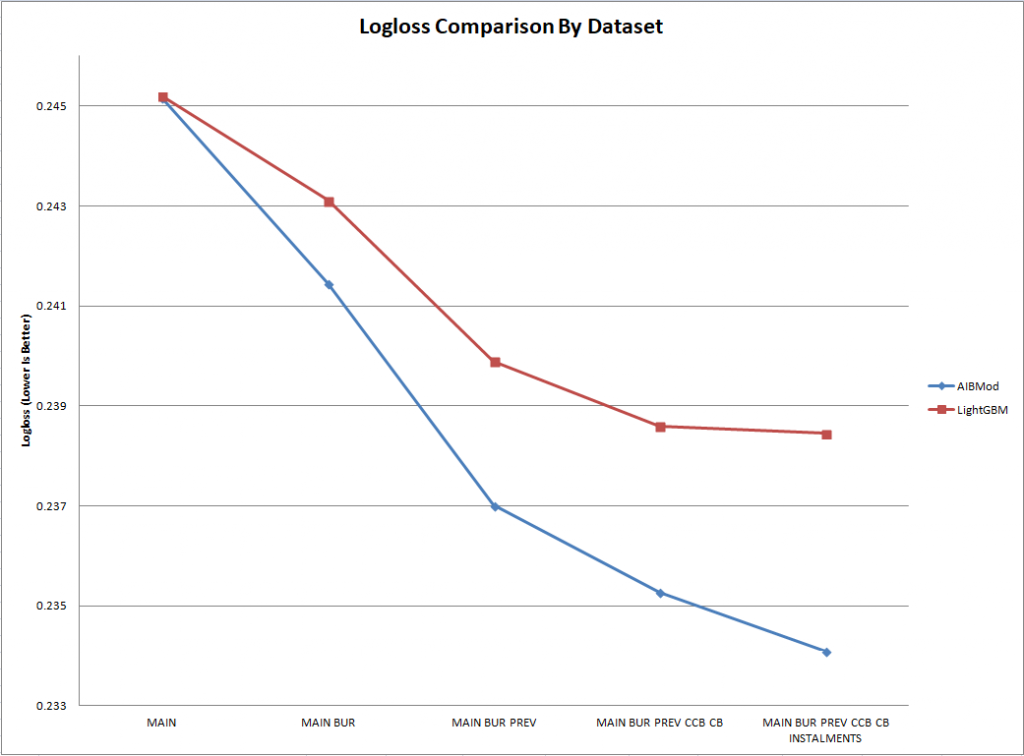
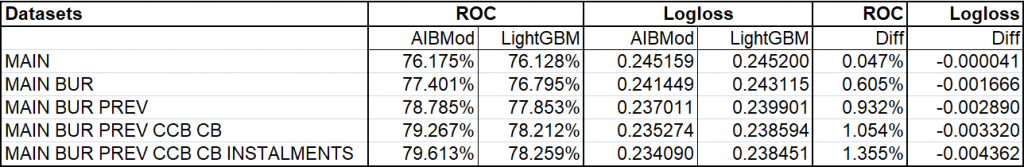
Table of Results Graphed Above
Results Discussion
The graphs and the table above clearly demonstrate that AIBMod has developed a model framework, based on the neural transformer architecture, which is able to process the unstructured inputs as they are.
In doing so, information embedded in the data structure is retained.
This contrasts starkly with the pre-processing required by most ‘structured data’ models to fit unstructured data into them.
With the base data file, which comprises a normal tabular structured input, the AIBMod model has a slight advantage over the boosted tree model.
However, with each unstructured data file that is added to the problem, the AIBMod model is able to extract a greater amount of information than the XGBoost model. Hence the performance of the AIBMod model improves at a greater rate when compared to the XGBoost model.
Description of Datasets
MAIN – The dataset comprised of 307,511 rows of tabular data with 120 numerical and categorical features. However, 47 features related to the apartment of the borrower and they added almost nothing to the performance of the LightGBM model so, in the interests of reducing the size of the research problem, they were omitted. Of the remaining 73 features, 46 were categorical and 27 were numerical.
The Kaggle team used five fold cross validation – meaning each fold had circa 246,009 rows of training data and 61,502 of validation data.
BUREAU – This mapped directly into the MAIN dataset – but sometimes more than one row in the BUREAU file map to one row in the MAIN file, and sometimes no rows in the BUREAU file map to a row in the MAIN file. The BUREAU file has 17 features – 5 categorical and 12 numerical.
PREV – This mapped directly into the MAIN dataset – but sometimes more than one row in the PREV file map to one row in the MAIN file, and sometimes no rows in the PREV file map to a row in the MAIN file. The PREV file has 35 features – 18 categorical and 17 numerical.
PREV CCB – This mapped directly into the PREV dataset – but sometimes more than one row in the PREV CCB file map to one row in the PREV file, and sometimes no rows in the PREV CCB file map to a row in the PREV file. The PREV CCB file has 20 features – 3 categorical and 17 numerical.
PREV CB – This mapped directly into the PREV dataset – but sometimes more than one row in the PREV CB file map to one row in the PREV file, and sometimes no rows in the PREV CB file map to a row in the PREV file. The PREV CB file has 8 features – 3 categorical and 5 numerical.
CCB INSTALMENT – This mapped directly into the PREV dataset – but sometimes more than one row in the CCB INSTA file map to one row in the PREV file, and sometimes no rows in the CCB INSTA file map to a row in the PREV file. The CCB INSTA file has 5 features – 0 categorical and 5 numerical.
CB INSTALMENT – This mapped directly into the PREV dataset – but sometimes more than one row in the CB INSTA file map to one row in the PREV file, and sometimes no rows in the CB INSTA file map to a row in the PREV file. The CB INSTA file has 6 features – 0 categorical and 6 numerical.
There was also an additional file, BUREAU BAL which mapped into the BUREAU file in a many to one or none to one basis, but this was not used in the research as for both the AIBMod and the LightGBM models it added very little to the overall performance. Again, in the interests of trying to build a model that was not unnecessarily complex, this file was removed from the research.
- ROC here means AUC ROC i.e. the area under the ROC curve ↩︎
